Summary
Fentanyl addiction has become a critical public health crisis, with overdose deaths rising sharply in recent years. This powerful synthetic opioid is highly addictive and requires specialized treatment approaches to ensure effective recovery. This article explores the nature of fentanyl addiction, the challenges it presents, and the most effective treatment options available. It also outlines practical recovery steps to help individuals and families navigate the journey toward lasting sobriety.
The rise of fentanyl in the illicit drug market has been alarming, as it is often mixed with other substances, increasing the risk of accidental overdose for users who may be unaware of its presence. Fentanyl is estimated to be 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine, which means even a small amount can lead to life-threatening consequences. This potency not only complicates the treatment landscape but also highlights the urgent need for public awareness and education about the dangers associated with its use. Many individuals struggling with addiction may initially turn to fentanyl as a means of managing pain or seeking euphoria, unaware of its highly addictive nature and the severe withdrawal symptoms that can ensue when trying to quit.
Moreover, the stigma surrounding opioid addiction often prevents individuals from seeking help, leaving families and communities grappling with the fallout of this crisis. Support systems, including counseling and peer support groups, play a vital role in recovery, as they provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences and challenges. Additionally, integrating mental health services into addiction treatment can address underlying issues such as anxiety or depression, which often accompany substance use disorders. As we delve deeper into the complexities of fentanyl addiction, it becomes increasingly clear that a multifaceted approach is essential for fostering resilience and promoting long-term recovery.
Understanding Fentanyl and Its Risks
Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that is 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine. Originally developed for pain management in medical settings, it has increasingly been found on the illicit drug market, often mixed with heroin or other substances without the user’s knowledge. This significantly increases the risk of overdose.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), synthetic opioids like fentanyl were involved in nearly 73% of opioid overdose deaths in 2019, a figure that has only grown since. The potency and rapid onset of fentanyl make it particularly dangerous, as even a tiny amount can cause respiratory depression and death. The drug’s presence in counterfeit pills and other street drugs has further complicated the landscape of substance abuse, leading many unsuspecting users to ingest lethal doses without realizing the danger they are in.
Understanding the risks associated with fentanyl is crucial for recognizing the urgency of seeking professional treatment and the need for tailored rehabilitation programs. This understanding can also foster greater awareness in communities about the signs of opioid addiction and the importance of harm reduction strategies, such as the availability of naloxone, a medication that can reverse opioid overdoses if administered in time.
Why Fentanyl Addiction Is Especially Challenging
Fentanyl’s high potency means that the physical dependence it creates is intense, and withdrawal symptoms can be severe. These symptoms often include:
- Extreme muscle and bone pain
- Severe cravings
- Intense anxiety and depression
- Gastrointestinal distress such as nausea and vomiting
- Insomnia and fatigue
Because of these symptoms, many individuals find it difficult to quit without professional help. Additionally, the risk of relapse is high due to fentanyl’s ability to quickly rewire brain chemistry. The psychological grip of fentanyl can lead to a cycle of addiction that is hard to break, as users may return to the drug to alleviate withdrawal symptoms or to recapture the euphoric high they once experienced. Furthermore, the stigma surrounding addiction can deter individuals from seeking the help they need, leaving them trapped in a dangerous cycle.

Moreover, the social and economic implications of fentanyl addiction extend beyond the individual. Families often bear the brunt of the emotional toll, facing challenges such as strained relationships and financial instability. Communities are also affected, as the rise in opioid-related incidents can lead to increased healthcare costs and a strain on local resources. Addressing fentanyl addiction requires a comprehensive approach that includes not only medical treatment but also community support and education to break the cycle of addiction and promote recovery.
Effective Treatment Options for Fentanyl Addiction
Treatment for fentanyl addiction must be comprehensive and individualized. The complexity of fentanyl dependence means that traditional opioid rehab methods may need to be adapted to address the unique challenges posed by this drug.
Medical Detoxification
Detox is the first critical step in fentanyl rehab. Due to the severity of withdrawal symptoms, medical supervision is essential. Detox programs often use medications to ease withdrawal and reduce cravings, including:
- Buprenorphine: A partial opioid agonist that reduces withdrawal symptoms and cravings without producing the same high.
- Methadone: A long-acting opioid agonist used to stabilize patients and ease withdrawal symptoms.
- Naltrexone: An opioid antagonist that blocks the effects of opioids and helps prevent relapse after detox.
Medical detox typically lasts from a few days to two weeks, depending on the individual’s level of dependence and overall health. During this period, patients may also receive supportive care, including hydration, nutritional support, and mental health evaluations, which are crucial for addressing any co-occurring disorders that may complicate recovery.
Inpatient Rehabilitation Programs for Fentanyl Addiction
Inpatient or residential rehab programs provide a structured environment where individuals can focus solely on recovery. These programs offer 24/7 medical care, therapy, and support, which is especially important for fentanyl addiction due to the risk of relapse and overdose.
Benefits of inpatient rehab include:
- Continuous medical monitoring
- Access to behavioral therapies
- Peer support from others in recovery
- Removal from triggers and high-risk environments

In addition to these benefits, inpatient programs often incorporate holistic approaches such as yoga, meditation, and art therapy, which can enhance emotional healing and provide patients with alternative coping strategies. The immersive nature of these programs allows individuals to build a strong foundation for recovery, fostering a sense of community and shared experience among participants.
Outpatient Treatment Options
For individuals with less severe addiction or those transitioning from inpatient care, outpatient programs can be effective. These programs allow patients to live at home while attending therapy sessions and medical appointments regularly.
Outpatient treatment often includes:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Medication-assisted treatment (MAT)
- Group counseling
- Family therapy
While outpatient programs offer more flexibility, they require strong personal motivation and a supportive home environment. Patients are encouraged to engage in community support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA), which can provide additional layers of accountability and encouragement. The combination of structured therapy and community support can significantly enhance the chances of long-term recovery.
Behavioral Therapies and Counseling
Behavioral therapies are a cornerstone of fentanyl addiction treatment. They help patients understand the psychological aspects of addiction, develop coping skills, and prevent relapse. Common therapies include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps patients identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to drug use.
- Contingency Management: Uses positive reinforcement to encourage sobriety.
- Motivational Interviewing: Enhances motivation to change and commit to treatment.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Focuses on emotional regulation and stress management.
These therapies are often tailored to meet the specific needs of the patient, taking into account their personal history, triggers, and emotional state. Additionally, family involvement in therapy can be beneficial, as it helps to mend relationships that may have been strained due to addiction and fosters a supportive environment for recovery. By addressing both individual and relational dynamics, behavioral therapies can significantly enhance the effectiveness of treatment and support sustainable recovery.
Steps to Recovery After Rehab
Recovery from fentanyl addiction is a lifelong process. Rehab provides the tools and foundation, but ongoing effort and support are necessary to maintain sobriety.
Developing a Strong Aftercare Plan
Aftercare is essential to prevent relapse. A comprehensive aftercare plan may include:
- Continued outpatient therapy
- Regular medical check-ups and medication management
- Participation in support groups such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA)
- Engagement in healthy lifestyle activities like exercise and mindfulness practices
Aftercare plans should be personalized and flexible to adapt to changing needs over time. This adaptability is crucial as individuals may face new challenges or stressors that arise post-rehab. Regularly revisiting and adjusting the plan can help ensure that it remains relevant and effective. Additionally, incorporating family members into the aftercare process can provide an extra layer of support, helping to reinforce the individual’s commitment to recovery.
Building a Support Network
Isolation can be a major trigger for relapse. Building a strong support network of family, friends, and peers in recovery is vital. Support groups provide a sense of community and shared experience, which can be incredibly empowering. These groups often serve as safe spaces where individuals can share their struggles and successes without judgment, fostering a sense of belonging that is crucial for emotional health.
Family involvement in therapy can also improve outcomes by addressing relational dynamics and fostering understanding. Open communication within families can help to rebuild trust and strengthen bonds that may have been strained during the addiction period. Engaging in family therapy sessions can also educate loved ones about the nature of addiction, equipping them with the tools to support their family member effectively.

Addressing Underlying Issues
Many individuals struggling with fentanyl addiction have co-occurring mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, or trauma. Addressing these underlying issues through integrated treatment improves the chances of long-term recovery. Understanding the root causes of addiction is essential, as it allows for targeted interventions that can lead to more sustainable outcomes.
Dual diagnosis treatment programs specialize in simultaneously treating addiction and mental health disorders, ensuring a holistic approach. These programs often utilize a combination of therapy modalities, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which can help individuals develop healthier thought patterns and coping strategies. Furthermore, incorporating holistic practices such as yoga, art therapy, or equine therapy can enhance emotional expression and resilience, making recovery a more enriching experience.
Preventing Relapse
Relapse is common but not a failure. Recognizing early warning signs and having strategies in place can help individuals stay on track. Effective relapse prevention includes:
- Identifying and avoiding triggers
- Developing healthy coping mechanisms
- Maintaining regular therapy sessions
- Using medications as prescribed
- Staying connected with support networks
Moreover, establishing a daily routine can provide structure and stability, which are essential for maintaining sobriety. Engaging in new hobbies or interests can also serve as a positive distraction and help build a fulfilling life outside of addiction. Regularly practicing self-care and mindfulness techniques can further enhance emotional regulation, making it easier to navigate the ups and downs of recovery. By proactively addressing potential challenges, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of relapse and continue on their path to healing.
Fentanyl Addiction Treatment at CBH in Florida
Fentanyl addiction is a complex and dangerous condition requiring specialized treatment and ongoing support. Successful recovery involves a combination of medical detox, behavioral therapies, and comprehensive aftercare. By understanding the unique challenges of fentanyl addiction and utilizing evidence-based treatment options, individuals can reclaim their lives and build a sustainable path to sobriety.
If you or a loved one is struggling with fentanyl addiction, seeking professional help as soon as possible is critical. Early intervention can save lives and provide hope for a healthier future.
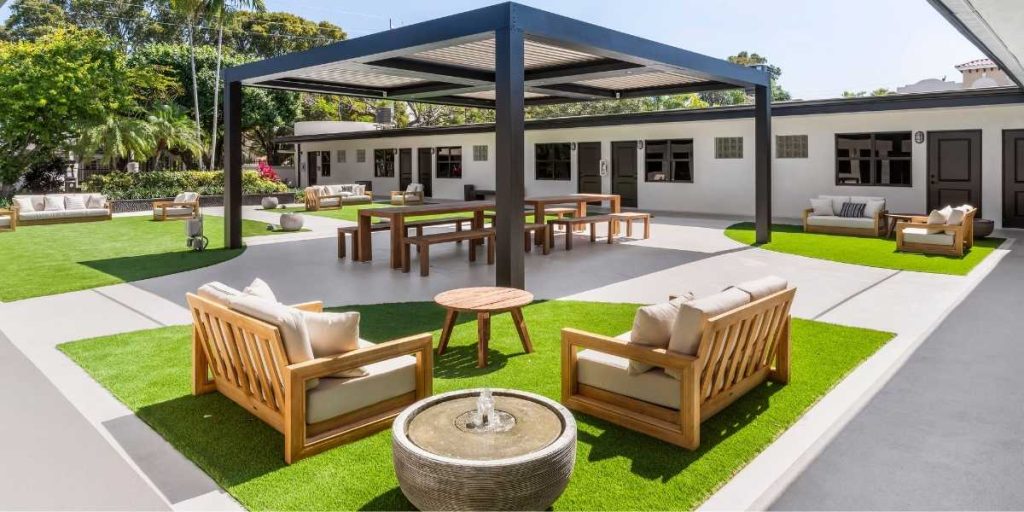

If you’re facing the challenges of fentanyl addiction, remember that you’re not alone. Compassion Behavioral Health is here to be your beacon of hope, offering personalized mental health and substance use treatment that paves the way for long-term, sustainable recovery. Our expert team in our South Florida rehab facility is committed to guiding you toward your highest physical and mental well-being through our tailored rehabilitation programs. Conveniently located near beautiful beaches and major airports, our Hollywood rehab center is a serene environment ideal for healing. Call Us Today and take the first step in reclaiming control of your life.



