Acute Stress Disorder (ASD) is a mental health condition that can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the symptoms associated with ASD, how it differs from other stress-related disorders, and the importance of seeking help. By the end of this article, readers will have a clearer picture of what to look for and how to cope with this challenging condition.
Understanding Acute Stress Disorder
Acute Stress Disorder is characterized by a range of psychological symptoms that arise within three days to four weeks following a traumatic event. While many people may experience temporary stress reactions, ASD can significantly impair an individual’s ability to function in daily life. Recognizing the symptoms early on is crucial for effective intervention and recovery. Symptoms can include intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety, which can lead to avoidance behaviors and emotional numbing. This heightened state of stress can affect personal relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life, making early intervention essential for those affected.
What Causes Acute Stress Disorder?

The primary trigger for ASD is exposure to a traumatic event. This can include:
- Natural disasters (e.g., earthquakes, floods)
- Serious accidents (e.g., car crashes, workplace incidents)
- Violent personal assaults (e.g., robbery, sexual assault)
- Witnessing a traumatic event (e.g., a violent crime, a loved one’s death)
While everyone reacts differently to trauma, those with a history of mental health issues or previous trauma may be more susceptible to developing ASD. Additionally, factors such as the severity of the trauma, the individual’s coping mechanisms, and the level of social support available can all influence the likelihood of developing this disorder. For instance, individuals who lack a strong support network may find it more challenging to process their experiences and may be at a higher risk for developing long-term psychological issues.
How is ASD Different from PTSD?
While both Acute Stress Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) arise from traumatic experiences, they differ primarily in duration and symptom onset. Key distinctions include:
- Onset: ASD symptoms appear within three days to four weeks after the trauma, whereas PTSD symptoms can develop anytime after the first month.
- Duration: ASD symptoms last for a minimum of three days and can persist for up to four weeks. If symptoms continue beyond this period, a diagnosis of PTSD may be considered.
Moreover, the nature of the symptoms can also vary between the two disorders. While ASD may involve dissociative symptoms, such as depersonalization or derealization, PTSD often includes a broader range of symptoms, including persistent negative alterations in mood and cognition. Understanding these differences is vital for mental health professionals in order to provide the appropriate treatment and support for individuals experiencing these distressing conditions. Early intervention strategies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can be particularly effective in addressing ASD symptoms and preventing the progression to PTSD.
Common Symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder
Recognizing the symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder is essential for timely intervention. Symptoms can be grouped into several categories, including intrusive memories, avoidance behaviors, negative mood, dissociation, and arousal. Each category encompasses various specific symptoms that can manifest in different ways.
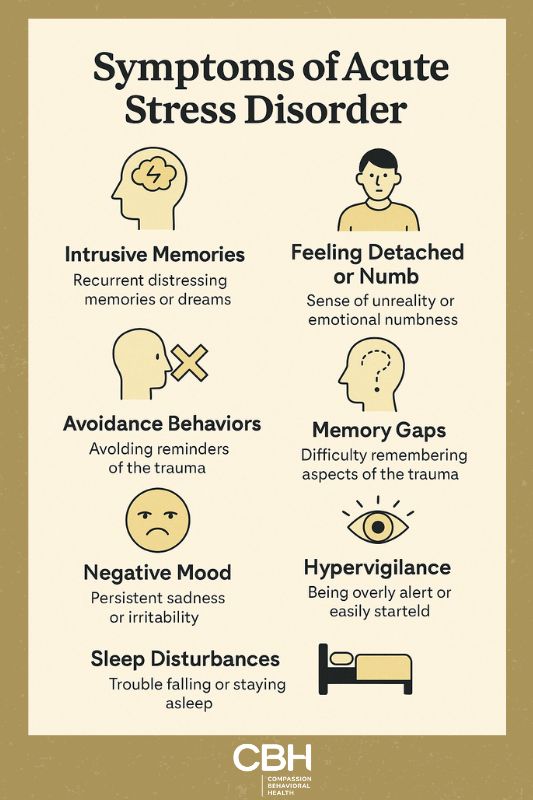
Intrusive Memories
One of the hallmark symptoms of ASD is the presence of intrusive memories related to the traumatic event. These can include:
- Recurrent, involuntary memories of the event
- Distressing dreams or nightmares
- flashbacks where the individual feels as though they are reliving the trauma
These intrusive memories can be overwhelming and may trigger intense emotional and physical reactions, making it difficult for individuals to cope with everyday tasks. The vividness of these memories can often feel as if the trauma is occurring in real-time, leading to heightened anxiety and distress. This can create a cycle where the individual becomes hyper-vigilant, constantly on guard for potential triggers, which can further exacerbate feelings of fear and helplessness.
Avoidance Behaviors
Individuals with ASD often engage in avoidance behaviors as a way to cope with their distress. This can manifest in several ways:
- Avoiding reminders of the trauma, such as places, people, or activities associated with the event
- Steering clear of conversations or discussions about the trauma
- Experiencing emotional numbness or detachment from others
While avoidance may provide temporary relief, it can hinder the healing process and exacerbate feelings of isolation. In some cases, individuals may also find themselves withdrawing from social interactions altogether, leading to a significant decline in their support network. This isolation can create a sense of loneliness, making it even more challenging to seek help or engage in therapeutic practices that could aid recovery.
Negative Mood
A negative mood is another common symptom of ASD. Individuals may experience:
- Persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness
- Difficulty experiencing positive emotions
- Increased irritability or anger
These emotional symptoms can affect personal relationships and overall quality of life, making it essential to address them promptly. The pervasive nature of these negative feelings can lead to a distorted perception of oneself and the world, often resulting in a lack of motivation to engage in previously enjoyed activities. This emotional turmoil can also strain relationships with family and friends, who may struggle to understand the individual’s experience, further contributing to a sense of alienation and despair.
Dissociative Symptoms
Dissociation is a common response to trauma, serving as a coping mechanism to detach from the distressing experience. Symptoms of dissociation in ASD may include:
Feeling Detached or Numb
Individuals may feel disconnected from themselves or their surroundings. This can manifest as:
- A sense of unreality regarding oneself or the environment
- Emotional numbness or a lack of responsiveness to emotional stimuli
This detachment can be disorienting and may contribute to feelings of confusion or anxiety. In some cases, individuals might describe their experiences as if they are observing their lives from a distance, akin to watching a movie rather than living it. This phenomenon can lead to a profound sense of isolation, as the individual feels as though they are not fully present in their own life. Such feelings can be exacerbated by external triggers, such as certain sounds or smells that remind them of the trauma, further enhancing their sense of detachment.
Memory Gaps
Some individuals may experience gaps in their memory surrounding the traumatic event. This can include:
- Inability to recall important aspects of the trauma
- Difficulty remembering events that occurred during the period of trauma
These memory lapses can further complicate the healing process, as individuals may struggle to make sense of their experiences. They might find themselves piecing together fragmented memories, which can lead to feelings of frustration and helplessness. Additionally, these gaps in memory can affect relationships, as loved ones may not understand why the individual cannot share their experience or may inadvertently trigger distress by bringing up topics related to the trauma. The struggle to reconcile these missing pieces can also lead to a sense of self-doubt, as individuals may question their own perceptions of reality and the validity of their experiences.
Arousal Symptoms
Arousal symptoms are characterized by heightened physiological responses and can significantly impact daily functioning. Common arousal symptoms include:
Hypervigilance
Individuals may become excessively alert and aware of their surroundings, leading to:
- Difficulty relaxing or feeling safe
- Exaggerated startle responses to unexpected stimuli
This constant state of alertness can be exhausting and may contribute to anxiety and irritability. The hypervigilant state often results in a heightened perception of threats, even in safe environments, which can make social interactions challenging. Individuals may find themselves avoiding crowded places or situations that they perceive as potentially dangerous, leading to social isolation and further exacerbating feelings of loneliness. The psychological toll of hypervigilance can also manifest in physical symptoms, such as muscle tension and headaches, as the body remains in a state of readiness for perceived danger.
Sleep Disturbances
Sleep problems are common among those with ASD. Symptoms may include:
- Insomnia or difficulty falling asleep
- Frequent awakenings during the night
- Restless sleep or nightmares
These disturbances can further exacerbate feelings of fatigue and emotional distress, creating a cycle that is difficult to break. The lack of restorative sleep can lead to cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with concentration, memory, and decision-making, which can hinder daily activities and responsibilities. Additionally, the emotional dysregulation associated with sleep disturbances can heighten irritability and mood swings, making it even more challenging for individuals to cope with stressors. Strategies to improve sleep hygiene, such as establishing a consistent bedtime routine and creating a calming sleep environment, can be beneficial, but often require time and patience to implement effectively.
Impact of Acute Stress Disorder on Daily Life
The symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder can significantly affect various aspects of an individual’s life. Understanding the potential impacts can help in recognizing the importance of seeking help.
Personal Relationships
ASD can strain personal relationships due to emotional withdrawal, irritability, and difficulty communicating. Friends and family may feel confused or helpless when trying to support their loved one, which can lead to further isolation. The emotional distance created by ASD can make it difficult for loved ones to connect, often resulting in misunderstandings and frustration on both sides. This can create a cycle of tension where the individual suffering from ASD feels increasingly alienated, while their support network feels powerless to bridge the gap.
Moreover, the unpredictability of emotional responses can lead to conflicts that might not have arisen otherwise. For instance, a seemingly minor disagreement can escalate into a major argument, fueled by the heightened sensitivity and stress levels experienced by the individual with ASD. This not only affects the immediate relationship but can also ripple out to affect social circles, as mutual friends may feel caught in the middle or unsure of how to engage with either party.
Work and Daily Functioning
Many individuals with ASD may find it challenging to concentrate, make decisions, or perform tasks at work or school. This can lead to:
- Decreased productivity
- Increased absenteeism
- Strained relationships with colleagues
As a result, individuals may experience feelings of inadequacy or frustration, further compounding their distress. The cognitive impairments associated with ASD, such as difficulty with memory and attention, can make even simple tasks feel overwhelming. This can lead to a vicious cycle where the fear of failure or making mistakes causes individuals to avoid responsibilities altogether, which only exacerbates their feelings of worthlessness.
Additionally, the workplace environment can become a source of anxiety. The pressure to meet deadlines or engage in teamwork can trigger symptoms of ASD, leading to panic attacks or emotional breakdowns. Colleagues may not understand the underlying issues, which can result in stigma or negative perceptions. This lack of understanding can further alienate the individual, making it even more challenging to navigate their professional life while coping with the symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder.
Seeking Help for Acute Stress Disorder
Recognizing the symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder is the first step toward recovery. Seeking help is crucial for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Therapeutic Approaches
Several therapeutic approaches can be effective in treating ASD, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This therapy helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping strategies.
- Exposure Therapy: Gradual exposure to trauma-related memories and situations can help reduce avoidance behaviors and desensitize individuals to triggers.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): This therapy involves processing traumatic memories through guided eye movements, helping individuals integrate and heal from their experiences.
Medication Options
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of ASD. Common options include:
- Antidepressants to alleviate mood disturbances
- Anxiolytics for anxiety relief
- Sleep aids to address insomnia
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Self-Care Strategies for Managing Symptoms

In addition to professional treatment, individuals can adopt self-care strategies to help manage symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder. These may include:
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help individuals reduce anxiety and improve emotional regulation. Techniques may include:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Yoga or tai chi
Incorporating these practices into daily routines can promote a sense of calm and well-being.
Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity can have a positive impact on mental health. Exercise can help reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance overall well-being. Activities may include:
- Walking or jogging
- Swimming
- Dancing or group fitness classes
Finding enjoyable activities can make it easier to stay active and reap the benefits.
Accute Stress Disorder Treatment in Florida

Acute Stress Disorder is a serious condition that can arise after experiencing trauma. Recognizing the symptoms early on is crucial for effective intervention and recovery. By understanding the various symptoms and seeking appropriate help, individuals can work toward healing and regaining control over their lives.
Whether through therapy, medication, or self-care strategies, support is available. It is essential for those affected to remember that they are not alone and that recovery is possible.
For anyone experiencing symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder, reaching out for help is a vital step toward healing and reclaiming a sense of normalcy in life.
If you or a loved one is navigating the challenges of Acute Stress Disorder, remember that Compassion Behavioral Health is here to offer the support and care you need. Our specialized team is committed to providing a customized approach to treatment, ensuring a path to long-term, sustainable recovery. Located in South Florida, our Hollywood rehab center is a place of solace and healing. Don’t hesitate to Call Us Today and take the first step towards reclaiming your well-being and embarking on your journey to recovery.



