What Is Addiction Treatment?
Addiction treatment includes various methods and programs used to help individuals who are struggling with addiction to substances or behaviors.
The goal of addiction treatment is to help individuals achieve and maintain sobriety, improve their health and social function, and manage or overcome the issues that led to the addiction.
The treatment is personalized and can include a combination of different approaches such as:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
- Dual Diagnosis
- Family Involvement
- Group Therapy
- Individual Therapy
- Motivational Interviewing
- Neurofeedback
- Relapse Prevention
- Solution-Focused Brief Therapy
- Virtual Therapy
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Who Might Need Addiction Treatment?
Addiction treatment is necessary for a wide range of individuals who struggle to control their substance use or behaviors, despite the negative consequences.
The common groups of people who might need addiction treatment are:
- Individuals with physical dependence: Those who experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop using a substance, indicating physical dependence, are usually suitable candidates for addiction treatment.
- People with chronic use patterns: Individuals who have been using substances for an extended period, especially those who need bigger doses over time to achieve the same effect (tolerance), often require treatment.
- Those experiencing negative consequences: If substance use is causing negative outcomes in their personal, professional, or academic life, treatment is needed.
- Individuals with co-occurring mental health disorders: Many people with addiction issues also have mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder. Treating both conditions simultaneously is crucial for effective recovery.
- Relapsed patients: Those who have attempted to stop using substances on their own but have relapsed may need more structured or intensive treatment.
- Individuals engaging in risky behaviors: This includes using substances in dangerous situations (like driving), using illegal drugs, or engaging in risky sexual behaviors.
Most Common Types of Addictions
Addiction can manifest in many forms, impacting individuals from all walks of life. From substance dependencies to behavioral compulsions, the nature of addiction is complex and varied.
Most common types of addictions include:
Alcohol Addiction
Alcohol addiction, or alcoholism, is characterized by the inability to control or stop alcohol use despite adverse social, occupational, or health consequences.
Amphetamine Addiction
Amphetamine addiction results from a strong reliance on stimulants such as amphetamines, leading to severe physical and psychological issues.
Benzodiazepine Addiction
Benzodiazepine addiction often develops from a prolonged use of benzodiazepines, prescribed for issues like anxiety or insomnia, leading to dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
Cocaine Addiction
Cocaine addiction is characterized by the compulsive use of cocaine, a powerful stimulant, leading to serious health and social problems.
Heroin Addiction
Heroin addiction is a severe form of opioid addiction characterized by dependence on heroin, accompanied by significant withdrawal symptoms when use is stopped.
Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction includes addiction to prescription opioids as well as illicit opioids like heroin, leading to physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
Sedative Addiction
Sedative addiction includes dependence on sedative-hypnotic drugs (like barbiturates and benzodiazepines) often prescribed for anxiety or sleep disorders.
Various Treatment Approaches for Addiction at CBH
Treating addiction involves various approaches tailored to each individual’s needs.
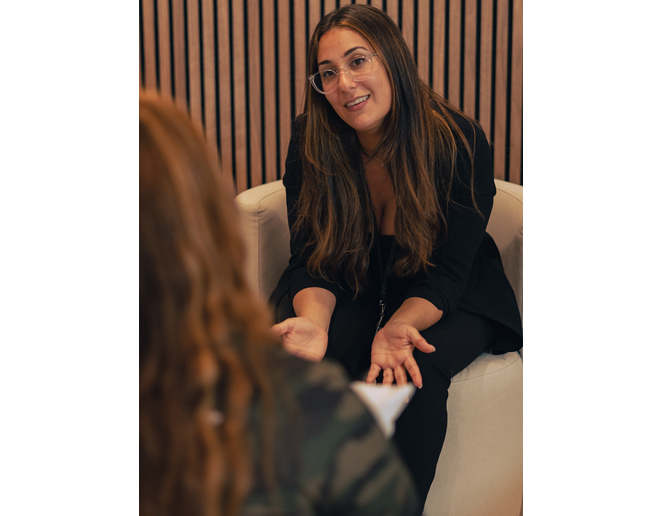

The key treatment methods include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A type of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors. It’s effective in treating a variety of addictions by teaching coping skills to manage triggers and prevent relapse.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): Originally developed for borderline personality disorder, DBT is effective in substance use treatment. It focuses on teaching skills in distress tolerance, emotion regulation, mindfulness, and interpersonal effectiveness.
- Dual Diagnosis: This approach treats individuals who have both a substance use disorder and a co-occurring mental health condition. The treatment addresses both issues simultaneously for effective recovery.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is used primarily to treat trauma and PTSD, which are often underlying issues in addiction. It involves processing traumatic memories while focusing on external stimuli like eye movements.
- Family Involvement: Family involvement includes the addict’s family in the treatment process. This can include family counseling and education to improve communication and support systems.
- Group Therapy: In group therapy, individuals share experiences and support each other under a therapist’s guidance. It’s beneficial for building social skills and learning from others’ experiences.
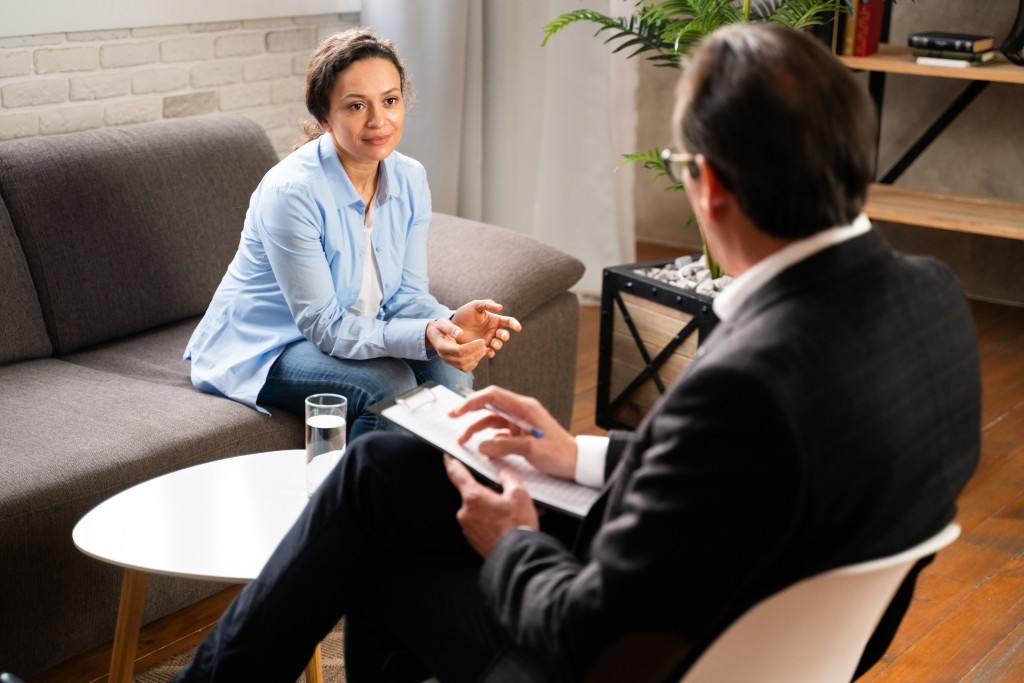
- Individual Therapy: One-on-one sessions with a therapist focus on the underlying issues of addiction. It allows for personalized attention and tailored therapeutic strategies.
- Motivational Interviewing (MI): MI is a client-centered approach that elicits behavioral change by helping clients explore and resolve ambivalence about their substance use.
- Neurofeedback: This therapy uses real-time displays of brain activity to teach self-regulation of brain function. It can be used to reduce symptoms of addiction, anxiety, and depression.
- Relapse Prevention: This approach involves identifying and managing high-risk situations, developing coping strategies, and maintaining lifestyle changes to prevent relapse.
- Solution-Focused Brief Therapy: This therapy focuses on what clients want to achieve through therapy rather than on past problems. It’s goal-directed and works well in short-term treatment scenarios.
- Virtual Therapy: Remote therapy sessions via video or phone calls. It’s convenient for those who cannot attend in-person sessions and has become more prevalent, offering flexibility and broader access to treatment.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): A non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. It’s used to treat depression, which can be a co-occurring disorder with addiction.
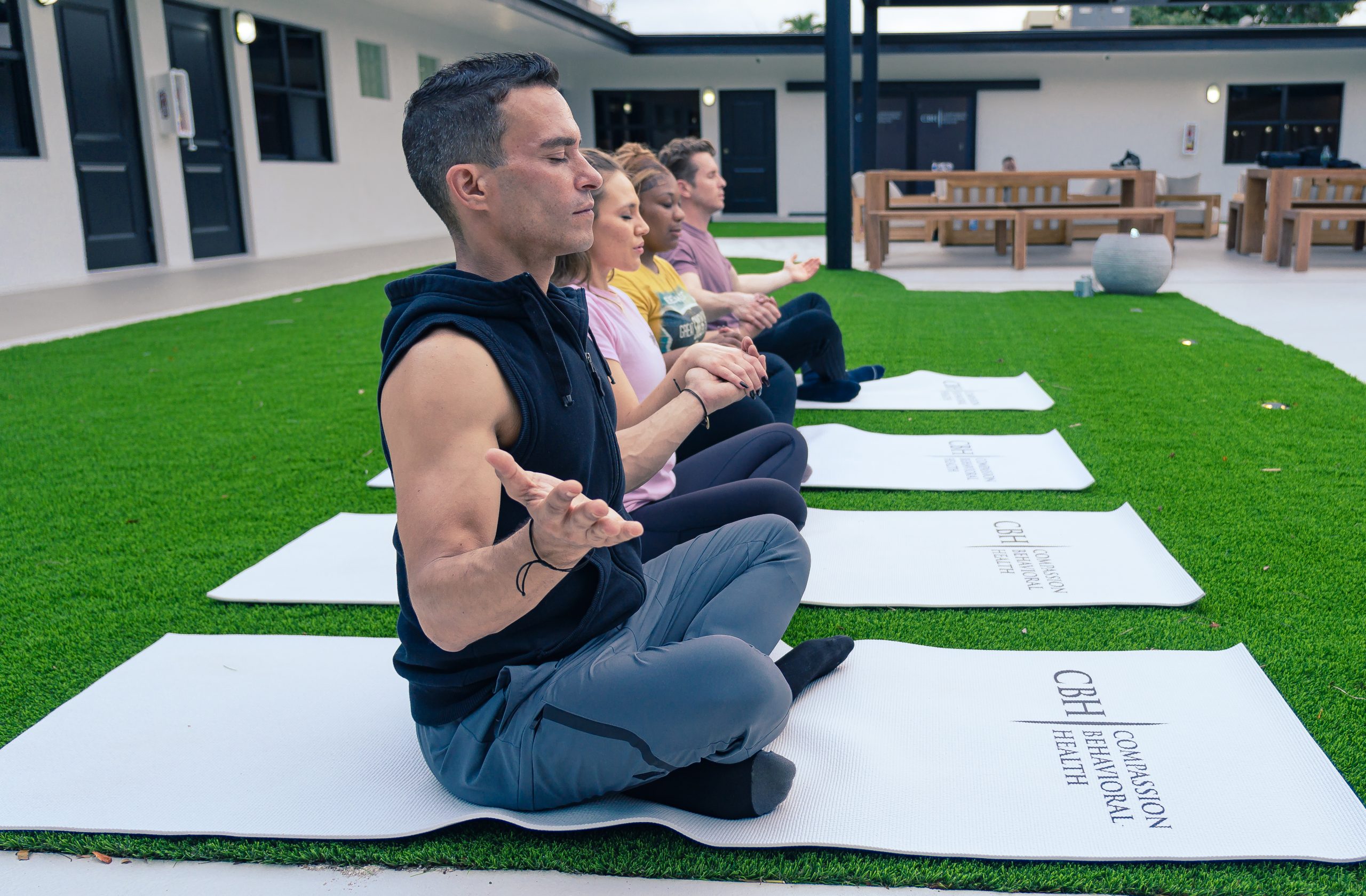
Addiction Treatment at CBH in South Florida

Compassion Behavioral Health (CBH) stands out as a top-rated center for mental health and substance abuse treatment in South Florida.
We are dedicated to helping people from all walks of life in overcoming addiction and striving towards healthier and more fulfilling lives.
Our state-of-the-art facilities are complemented by a team of dedicated and empathetic professionals who are not just experts in their field, but also deeply committed to providing compassionate care.
Recognizing the integral role of family in the recovery process, our programs incorporate family involvement. We believe in not only treating our patients but also in building a robust post-treatment support system that includes family therapy.
This approach extends beyond the clinical setting, as we continue to offer support and guidance even after our clients begin their journey with Compassion Behavioral Health. Our aim is to be the best in the field, not just in treatment delivery, but also in ensuring a supportive environment for our clients and their families.