Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a complex mental health condition that affects individuals across genders. While it is often associated with women, it is crucial to recognize that men can also experience BPD. In this article, we will delve into the realm of Borderline Personality Disorder in men, exploring its definition, diagnostic criteria, prevalence, impact on men’s lives, the intersection of masculinity, and available treatment options.
Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder
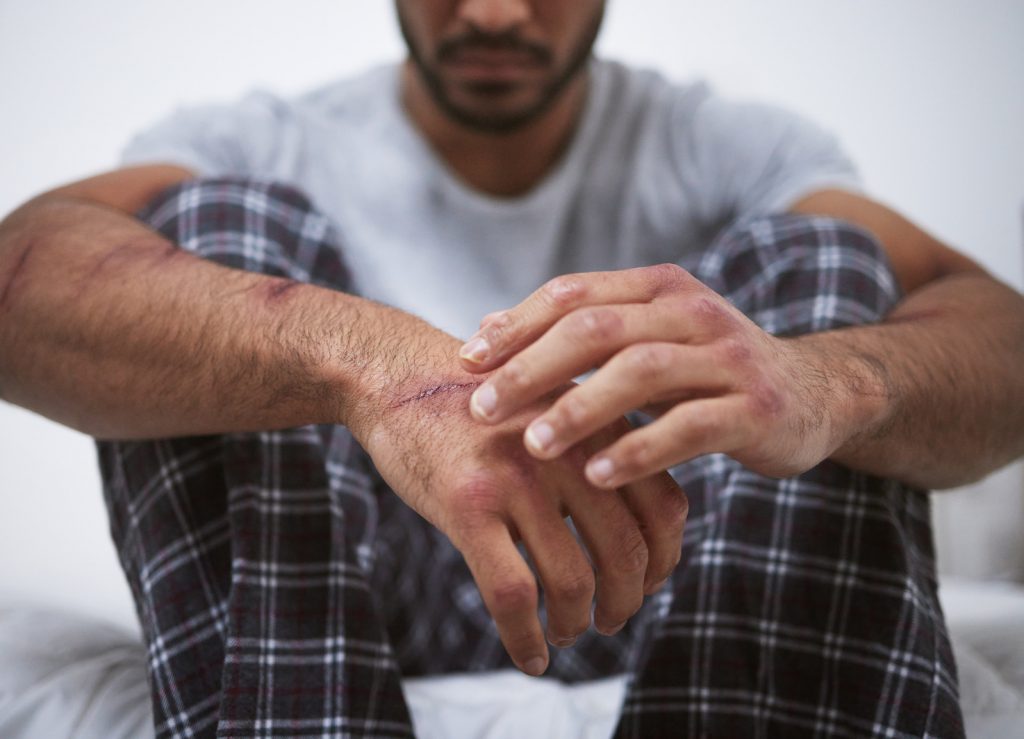

Before delving deeper into Borderline Personality Disorder in men, let us first understand what this condition entails. BPD is characterized by intense emotional instability and difficulties in maintaining stable relationships. Individuals with BPD often experience intense fear of abandonment, rapid mood swings, unstable self-image, and impulsive behaviors. These symptoms can significantly disrupt daily functioning and interpersonal relationships.
Borderline Personality Disorder is a complex mental health condition that affects a significant number of individuals worldwide. It is important to note that BPD can occur in both men and women, although it may present differently in each gender. Understanding the key characteristics and diagnostic criteria of BPD is crucial in order to provide appropriate support and treatment to those affected.
Key Characteristics of Borderline Personality Disorder
Individuals with BPD may exhibit several key characteristics, including emotional dysregulation, unstable relationships, self-destructive behaviors, and a chronic feeling of emptiness. Emotional dysregulation refers to the difficulty in managing and controlling one’s emotions, which can lead to extreme mood swings and intense emotional reactions. Unstable relationships are another hallmark of BPD, as individuals with this condition often struggle with maintaining healthy and consistent connections with others.

Self-destructive behaviors, such as self-harm or substance abuse, are common among individuals with BPD. These behaviors often serve as coping mechanisms to alleviate emotional pain or regulate intense emotions. Additionally, individuals with BPD may experience a chronic feeling of emptiness, as if something is missing from their lives. This feeling of emptiness can contribute to a sense of dissatisfaction and a constant search for validation and fulfillment.
Common Symptoms of BPD
The symptoms of BPD can vary significantly from person to person, but some common signs include:
- Intense and unstable relationships
- Fear of abandonment
- Unstable self-image
- Impulsive behaviors (e.g., spending sprees, substance abuse)
- Recurrent suicidal behavior or self-harm
- Emotional instability
- Chronic feelings of emptiness
- Difficulty controlling anger
The Diagnostic Criteria for Borderline Personality Disorder
In order to receive a diagnosis of Borderline Personality Disorder, individuals must meet specific criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). These criteria include a pervasive pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and emotions, as well as marked impulsivity. It is important to note that these symptoms must be present for a significant period of time and must cause significant distress or impairment in functioning.
Furthermore, the diagnostic process should be carried out by a trained mental healthcare professional who can conduct a comprehensive assessment, taking into account the individual’s history, symptoms, and overall functioning. It is crucial to rule out other potential causes for the symptoms, as BPD can often coexist with other mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, or substance use disorders.
By understanding the key characteristics and diagnostic criteria of Borderline Personality Disorder, we can better recognize and support individuals who may be struggling with this condition. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can make a significant difference in the lives of those affected, helping them to manage their symptoms, improve their relationships, and enhance their overall well-being.
Challenges in Diagnosis
Diagnosing BPD in men can be particularly challenging due to societal norms and expectations regarding masculinity. Men are often socialized to suppress their emotions, which can lead to a lack of awareness about their mental health struggles. As a result, symptoms may manifest in less recognizable ways, such as irritability or aggression, rather than the emotional volatility typically associated with BPD.
Additionally, men may be less likely to seek help for mental health issues, further complicating the diagnosis. It is crucial for mental health professionals to be aware of these gender differences when assessing and diagnosing BPD. Understanding the unique ways in which men may experience and express their symptoms can lead to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans that address their specific needs.
Moreover, the intersection of BPD with other mental health disorders, such as depression or anxiety, can further complicate the diagnostic process. Many individuals with BPD also experience co-occurring conditions, which can mask or mimic the symptoms of BPD, making it essential for clinicians to conduct comprehensive evaluations. This holistic approach not only aids in accurate diagnosis but also paves the way for effective therapeutic interventions that can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected.
The Prevalence of Borderline Personality Disorder in Men
Contrary to popular belief, Borderline Personality Disorder is not exclusive to women. While historically it has been more commonly associated with women, recent research suggests that BPD is prevalent in both genders. However, due to various societal factors, the diagnosis of BPD in men may be underreported.
Debunking the Myth of Gender Bias in Diagnosis

Gender bias can play a role in the underdiagnosis of Borderline Personality Disorder in men. The symptoms of BPD may be perceived as more acceptable or expected in women, leading to a potential overlooking of these symptoms in men. It is crucial to recognize and address this bias to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate support for individuals.
When it comes to mental health, gender biases can have significant consequences. Society often perpetuates the stereotype that women are more emotional and prone to mood swings, while men are expected to be stoic and in control of their emotions. These societal expectations can create a barrier for men with Borderline Personality Disorder, as their symptoms may not align with the traditional notion of masculinity.
Furthermore, the diagnostic criteria for Borderline Personality Disorder itself may be biased towards women. The symptoms of BPD, such as intense fear of abandonment, unstable relationships, and emotional instability, are often associated with women. This association can lead to a lack of recognition and understanding of these symptoms in men, resulting in underdiagnosis.
Understanding the Statistics
While it is difficult to ascertain the exact prevalence of Borderline Personality Disorder in men, studies indicate that approximately 38% of individuals diagnosed with BPD are men. However, it is worth noting that this number may vary depending on individual cultural and societal factors.
Research suggests that men with Borderline Personality Disorder may present with different symptoms compared to women. While women with BPD often exhibit emotional dysregulation and self-harming behaviors, men may display more externalizing behaviors, such as aggression and substance abuse. These differences in symptom presentation can further contribute to the underdiagnosis of BPD in men, as their symptoms may be misattributed to other conditions.
It is important to recognize that the prevalence of Borderline Personality Disorder in men is not a reflection of the severity or impact of the disorder. Men with BPD still experience significant distress and impairment in their daily lives. By raising awareness about the prevalence of BPD in men, we can promote early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment for all individuals affected by this complex disorder.
Potential Causes of BPD in Men
The exact cause of Borderline Personality Disorder remains unclear, but research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors may contribute to its development. Understanding these factors can help in both prevention and treatment.
Genetic Factors
Studies have shown that BPD can run in families, indicating a potential genetic predisposition. While no single gene has been identified as responsible for BPD, certain inherited traits, such as emotional sensitivity and impulsivity, may increase the likelihood of developing the disorder. Furthermore, research into the heritability of personality disorders suggests that individuals with a family history of BPD or related disorders may be more susceptible to experiencing similar emotional and behavioral challenges. This genetic link underscores the importance of considering family dynamics and mental health history when assessing risk factors for BPD.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors, particularly those experienced during childhood, can significantly impact the development of BPD. Some of these factors include:
- Childhood trauma (e.g., abuse, neglect)
- Parental separation or loss
- Unstable family dynamics
These experiences can shape an individual’s emotional regulation and coping mechanisms, potentially leading to the development of BPD symptoms in adulthood. In addition to these factors, the social environment, including peer relationships and community stability, can also play a critical role. For instance, boys who grow up in environments where emotional expression is discouraged may struggle to develop healthy coping strategies, which can exacerbate feelings of isolation and frustration. Moreover, societal expectations regarding masculinity can further complicate emotional expression, leading to a higher risk of developing maladaptive behaviors associated with BPD.
Moreover, the impact of cultural factors cannot be overlooked. Different cultures may have varying attitudes towards mental health, emotional expression, and family dynamics. In some cultures, discussing mental health issues may be stigmatized, preventing individuals from seeking help or support. This lack of access to mental health resources can lead to a cycle of untreated symptoms and worsening conditions. Understanding the interplay between cultural background and the development of BPD in men is essential for creating effective treatment strategies that are sensitive to individual experiences and societal norms.
The Impact of Borderline Personality Disorder on Men’s Lives
Borderline Personality Disorder can have profound effects on various aspects of men’s lives, ranging from emotional implications to social consequences and occupational challenges.
Emotional Implications
Men with BPD may face significant emotional turmoil. Intense mood swings, a fear of abandonment, and difficulties regulating emotions can lead to feelings of frustration, anger, and hopelessness. Seeking appropriate support and therapy can help individuals navigate these emotional challenges.
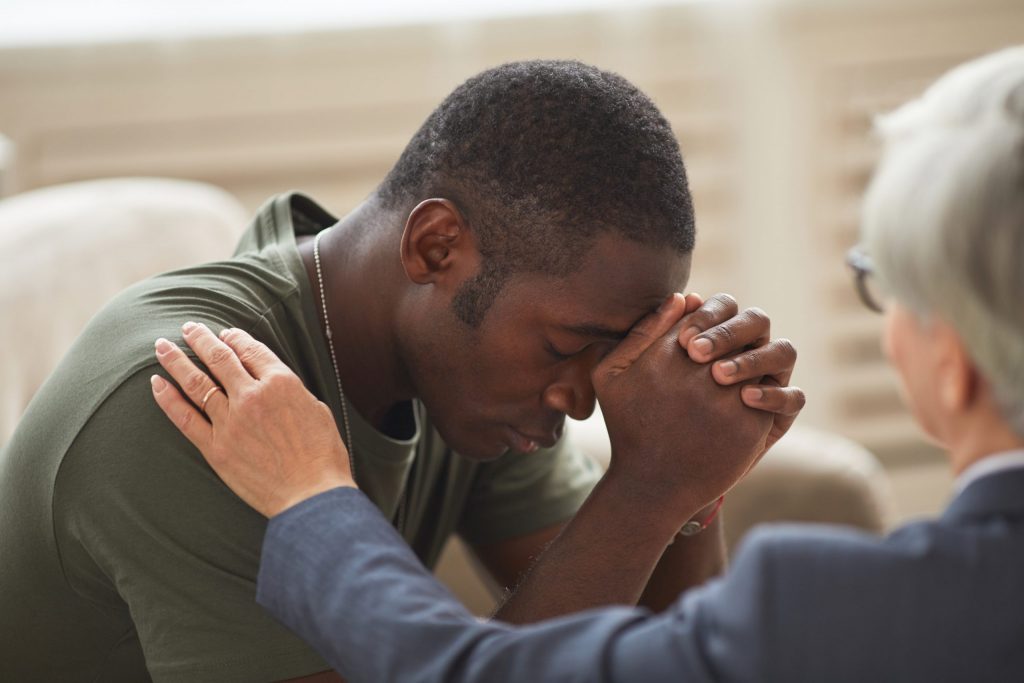

Social Consequences
BPD can impact men’s relationships, making it challenging to form and maintain stable connections. Difficulties with trust, impulsivity, and a fear of rejection may contribute to strained relationships, isolation, and feelings of loneliness. Developing healthy coping mechanisms and seeking therapy can aid in improving social interactions.
Occupational and Financial Challenges
Borderline Personality Disorder may also affect men in their professional lives. Difficulties with emotional regulation, impulse control, and maintaining stable routines can lead to challenges in work settings. In some cases, individuals may struggle with financial stability due to impulsive spending tendencies. Seeking occupational support and therapy can assist in managing these challenges.
The Intersection of Masculinity and Borderline Personality Disorder
Societal Expectations and Mental Health
Societal expectations of masculinity can influence how men perceive and seek help for mental health conditions such as BPD. The pressure to appear strong and self-reliant can make it difficult for men to acknowledge and address their emotional struggles. It is important to challenge these expectations and promote mental health awareness and support for men.
The Role of Masculinity in Symptom Presentation

The manifestation of BPD symptoms may be influenced by societal norms surrounding masculinity. Men with BPD may exhibit symptoms differently, such as increased irritability or aggression, compared to women. Raising awareness about these differences can help professionals provide better-targeted support and treatment.
Treatment Options for Men with Borderline Personality Disorder
Psychotherapy and Counseling

Psychotherapy, particularly dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), has shown effectiveness in treating Borderline Personality Disorder. DBT focuses on enhancing emotional regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, distress tolerance, and mindfulness. Seeking therapy, individual or group, tailored to men’s experiences can significantly improve their well-being.
Medication Management
While medication is not the sole treatment for BPD, it can be beneficial in managing specific symptoms such as depression, anxiety, or impulsivity. It is important to work closely with a mental healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication options if needed.
Lifestyle Changes and Coping Strategies

In addition to therapy and medication, certain lifestyle changes and coping strategies can help men with BPD manage their symptoms. Regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, practicing relaxation techniques, and engaging in activities that promote self-care and fulfillment contribute to overall well-being.
Get a Free Assessment for Borderline Personality Disorder
It is crucial to recognize and understand Borderline Personality Disorder in men to provide appropriate support and treatment. By debunking misconceptions, addressing gender bias in diagnosis, and promoting mental health awareness, we can empower men to seek help and lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by BPD.

At Compassion Behavioral Health, we offer a range of specialized treatment options tailored to the unique challenges that men with Borderline Personality Disorder face. Our multidisciplinary team employs evidence-based therapies such as Dialectical Behavioral Therapy, Mentalization-Based Therapy, and Transference-Focused Therapy, among others, to provide comprehensive care. With a focus on individualized treatment plans, we aim to equip men with the skills and strategies they need to manage their symptoms effectively. In our supportive and confidential environment, men can begin the journey to better mental health, learning to navigate the complexities of BPD while building healthier relationships and improving their overall quality of life. Call us at 844-503-0126 or contact us online today to get your free, quick assessment.