Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by extreme shifts in mood, energy levels, and behavior. While there are several types of bipolar disorder, the two most common are bipolar 1 and bipolar 2. Although they share similarities, there are distinct differences between the two that are important to understand.
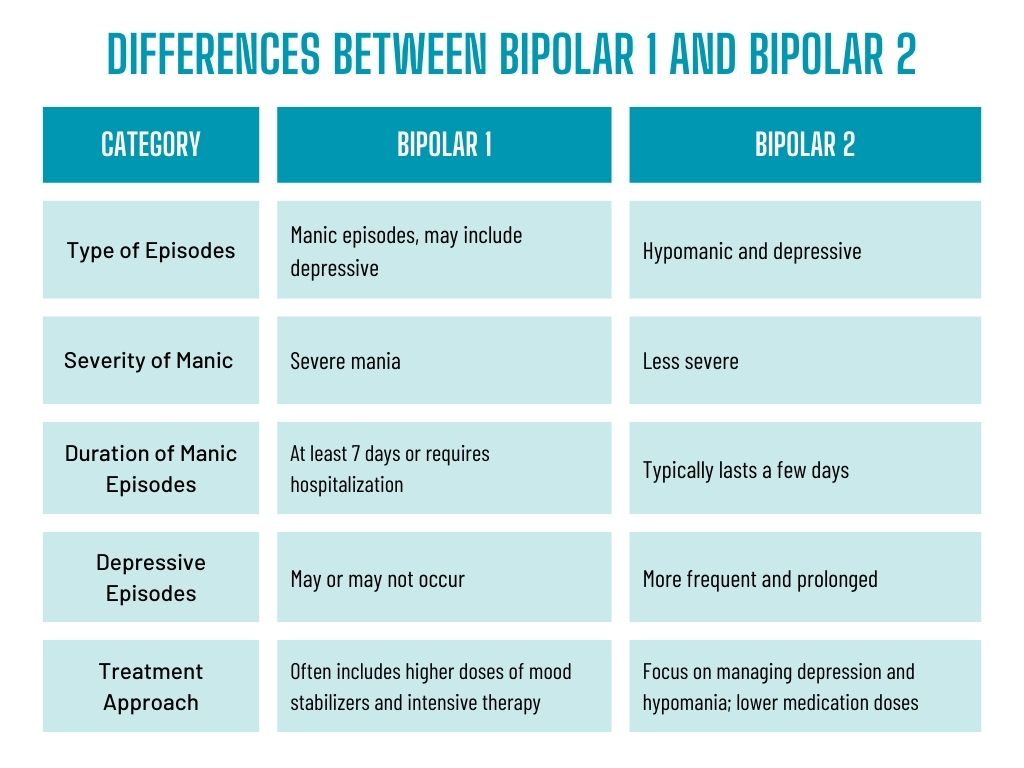
In short, the main differences between bipolar 1 and bipolar 2 are the severity and duration of manic episodes. Bipolar 1 involves more severe manic episodes that can last for several days or weeks, while bipolar 2 has less severe hypomanic episodes that typically last for a shorter duration.
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a chronic condition that affects the brain’s ability to regulate mood. People with bipolar disorder experience intense emotional highs, known as mania or hypomania, and depressive lows. These mood swings can significantly impact daily life and relationships.
Living with bipolar disorder can be a rollercoaster ride. Imagine waking up one morning feeling like you can conquer the world, full of energy and ideas. You might find yourself talking a mile a minute, making impulsive decisions, and taking on multiple projects at once. This is the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
During a manic episode, individuals may feel invincible, believing they have limitless abilities and talents. They might engage in risky behaviors, such as excessive spending, reckless driving, or engaging in promiscuous activities. While it may seem exciting at first, the consequences of these actions can be severe and long-lasting.
On the other end of the spectrum lies the depressive phase of bipolar disorder. Imagine waking up feeling empty, hopeless, and overwhelmed by sadness. You might find it difficult to get out of bed, lose interest in activities you once enjoyed, and struggle to concentrate. This is the depressive phase of bipolar disorder.
Depressive episodes can be debilitating, making it challenging to maintain relationships, perform well at work or school, and engage in self-care. The constant shift between these extreme emotional states can be exhausting and take a toll on both the individual with bipolar disorder and their loved ones.
The Basics of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a complex condition that can vary in severity and presentation from person to person. It typically begins in late adolescence or early adulthood and is characterized by episodes of mania, hypomania, and depression. Manic episodes involve elevated mood, increased energy, and impulsive behavior, while depressive episodes include feelings of sadness, worthlessness, and a loss of interest in activities.
Diagnosing bipolar disorder can be challenging as its symptoms can overlap with other mental health conditions. Mental health professionals rely on careful observation, interviews, and a thorough assessment of the individual’s history to make an accurate diagnosis.

Once diagnosed, treatment for bipolar disorder usually involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Medications, such as mood stabilizers and antipsychotics, help regulate mood and prevent extreme highs and lows. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or psychoeducation, can provide individuals with coping strategies and support to manage their symptoms effectively.
It’s important to note that bipolar disorder is a lifelong condition, and managing it requires ongoing care and support. With the right treatment plan and a strong support system, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead fulfilling and productive lives.
Common Misconceptions About Bipolar Disorder
Many misconceptions about bipolar disorder contribute to stigma and misunderstanding. One common misconception is that bipolar disorder is simply a mood swing or a personal weakness. In reality, bipolar disorder is a complex neurobiological condition that requires a comprehensive treatment approach.
Contrary to popular belief, bipolar disorder is not a character flaw or a result of personal weakness. It is a medical condition that affects the brain’s chemistry and functioning. Just like any other chronic illness, such as diabetes or asthma, bipolar disorder requires proper management and treatment to minimize its impact on an individual’s life.
Another misconception is that bipolar disorder is a rare condition. While it is true that bipolar disorder affects a smaller percentage of the population compared to conditions like depression or anxiety, it is still a relatively common mental health condition. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately 2.8% of adults in the United States have been diagnosed with bipolar disorder.
It’s important to challenge these misconceptions and promote a better understanding of bipolar disorder. By educating ourselves and others, we can create a more compassionate and supportive society for individuals living with this condition.
Bipolar 1
Bipolar 1 is the most severe form of bipolar disorder. It is characterized by manic episodes that last at least seven days or are severe enough to require hospitalization. These manic episodes may be accompanied by depressive episodes or periods of relative stability.
Defining Bipolar 1
Bipolar 1 is diagnosed when a person experiences a manic episode, which may be followed by depressive episodes. During a manic episode, individuals may display symptoms such as elevated mood, increased energy, racing thoughts, decreased need for sleep, and reckless behavior.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Bipolar 1

Diagnosing bipolar 1 involves a thorough evaluation of a person’s symptoms and history. A healthcare professional will assess the presence and duration of manic and depressive episodes and examine any previous psychiatric diagnoses or treatment history. Common symptoms of bipolar 1 include grandiosity, impulsivity, irritability, and a decreased need for sleep.
It is essential to rule out other possible causes for mood swings, such as substance abuse or medical conditions, before making a bipolar 1 diagnosis. A comprehensive assessment is crucial to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Furthermore, individuals with bipolar 1 may experience additional symptoms during manic episodes, such as increased talkativeness, distractibility, and engaging in activities with a high potential for painful consequences. These symptoms can significantly impact daily functioning and interpersonal relationships.
Treatment Options for Bipolar 1
Managing bipolar 1 involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Medications such as mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants may be prescribed to help stabilize mood and manage symptoms. Psychotherapy, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and family-focused therapy, can provide valuable support and teach coping strategies.

Moreover, individuals with bipolar 1 may benefit from participating in support groups or joining online communities where they can connect with others who share similar experiences. These platforms can offer a sense of belonging and understanding, reducing feelings of isolation often associated with mental health conditions.
In addition to medical interventions, self-care is an essential aspect of managing bipolar 1. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress can help minimize mood episodes and promote overall well-being.
It is worth noting that treatment for bipolar 1 is highly individualized, as different approaches may work better for different individuals. A collaborative approach between the individual, healthcare professionals, and support networks is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan.
In conclusion, bipolar 1 is a complex mental health condition characterized by severe manic episodes and potential depressive episodes. While it can significantly impact an individual’s life, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and support, individuals with bipolar 1 can lead fulfilling and productive lives.
Bipolar 2
Bipolar 2 is a less severe form of bipolar disorder. While it shares similarities with bipolar 1, there are key differences in the duration and intensity of manic and depressive episodes.
Living with bipolar 2 can be challenging, as individuals navigate the highs and lows of their mood swings. It is important to understand the nuances of this condition to effectively manage its symptoms and maintain stability.
Defining Bipolar 2

Bipolar 2 is diagnosed when a person experiences recurrent depressive episodes and at least one hypomanic episode. Hypomania is a less severe form of mania characterized by a distinct period of elevated mood, increased energy, and heightened creativity.
During a hypomanic episode, individuals may feel a surge of productivity and creativity. They may have an abundance of ideas and engage in goal-directed activities with enthusiasm. However, it is important to note that these episodes are not without their challenges. The increased energy and impulsivity can sometimes lead to risky behaviors or strained relationships.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Bipolar 2
Diagnosing bipolar 2 involves assessing the presence of depressive and hypomanic episodes. People with bipolar 2 may experience prolonged periods of depression, lasting weeks or months, interspersed with shorter episodes of hypomania.
During a depressive episode, individuals may feel overwhelming sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life.
On the other hand, during a hypomanic episode, individuals may exhibit symptoms such as increased talkativeness, racing thoughts, impulsivity, and an inflated sense of self-confidence. These symptoms are less severe than those experienced during a manic episode in bipolar 1.
It is important to note that bipolar 2 can sometimes be misdiagnosed as a major depressive disorder, as individuals may seek treatment only during their depressive episodes. However, a thorough evaluation by a mental health professional is necessary to accurately diagnose and differentiate between the two conditions.
Treatment Options for Bipolar 2
The treatment approach for bipolar 2 is similar to that of bipolar 1. Medications, including mood stabilizers and antidepressants, may be prescribed to manage symptoms and stabilize mood. Individuals need to work closely with their healthcare provider to find the right combination of medications that work best for them.
Therapy, such as psychoeducation and individual counseling, can also play a crucial role in the treatment of bipolar 2. These therapeutic interventions can help individuals understand their condition, develop coping skills, and maintain stability. Additionally, therapy can provide a safe space for individuals to explore their emotions and work through any challenges they may face.

Self-care is also crucial for individuals with bipolar 2. Establishing consistent routines, managing stress, and engaging in activities that promote emotional well-being can all contribute to symptom management and overall mental health. Individuals need to prioritize self-care and make it a part of their daily routine.
Support from loved ones can also make a significant difference in the life of someone with bipolar 2. Having a strong support system can provide emotional support, understanding, and encouragement during both the highs and lows of the condition. Get some tips to learn how to talk to someone with bipolar disorder
In conclusion, bipolar 2 is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to treatment and management. By understanding the symptoms, seeking appropriate help, and implementing effective strategies, individuals with bipolar 2 can lead fulfilling and stable lives.
Key Differences Between Bipolar 1 and Bipolar 2
While both bipolar 1 and bipolar 2 involve shifts in mood, energy, and behavior, there are several key differences between the two.
Symptom Severity and Duration
One of the significant distinctions between bipolar 1 and bipolar 2 is the severity and duration of manic and depressive episodes. In bipolar 1, manic episodes are more severe and can last for several days or weeks. In contrast, hypomanic episodes in bipolar 2 are less severe and typically last for a shorter duration.
Impact on Daily Life
Because of the intensity and duration of manic episodes, bipolar 1 may have a more significant impact on an individual’s daily life. The impulsive behavior and decreased need for sleep often associated with mania can disrupt relationships, work or school performance, and overall functioning. While bipolar 2 can still significantly affect daily life, the impact may be somewhat less severe.
Treatment Approach Differences
While the treatment approach for both bipolar 1 and bipolar 2 involves medication and therapy, there may be variations in the specific interventions used. Due to the more severe nature of bipolar 1, individuals may require higher medication doses and more intensive therapy. Additionally, the focus of therapy for bipolar 1 may include addressing the impact of manic episodes on personal and professional relationships.
On the other hand, the treatment approach for bipolar 2 may prioritize symptom management during depressive episodes while also addressing the potential risks associated with hypomania, such as impulsive decision-making.
In conclusion, bipolar disorder is a complex condition with different subtypes that require specific attention. Understanding the differences between bipolar 1 and bipolar 2 is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. With the appropriate support and management strategies, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead fulfilling lives and achieve improved stability and well-being.
Get Tailored Bipolar Disorder Treatments at CBH
At Compassion Behavioral Health, we are dedicated to empowering individuals with bipolar disorder to achieve lasting stability and lead fulfilling lives. Our compassionate and experienced team is here to provide the guidance and support needed to navigate the challenges of bipolar disorder.
If you or a loved one is struggling with bipolar disorder, please reach out to us for a confidential assessment and personalized bipolar disorder treatment recommendations.



